Your two kidneys are:
Under the lower ribs in the back of the body above the waist.
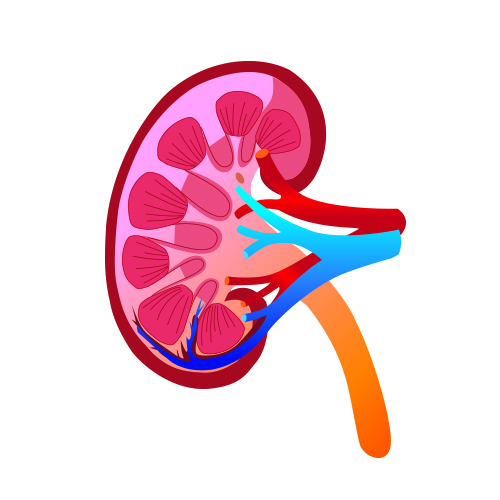
The kidneys are two bean-shaped organs

Each of your kidneys is made up of about 1 million filtering units called “nephrons”.
Functions of kidney
- Remove waste products from the body
- Balance the body fluids and electrolytes
- Release hormone that regulate blood pressure
- Control the production of red blood cells
- Produce active form of vitamin D for bones
What is the definition of “CKD – chronic kidney disease”?

- Evidence of kidney damage that is present for >3 months
- Detected by urine and blood tests as well as radiological examination (ultrasound scan)
Risk factors of CKD
- Diabetes mellitus
- Hypertension
- Obesity
- Use of nephrotoxic drugs (eg NSAIDS painkillers) or unrecognized supplements
- Age > 65 years
- Cardiovascular disease
- Gout and metabolic syndrome
- Kidney stones or prostate
- Inflammation – glomerulus
- Systemic or autoimmune disease (eg. Systemic lupus erythematosus)
- Family history of kidney disease
Signs and symptoms of CKD
Most of the patients do not have symptoms at early stage. If the kidney function is less than 30%, the following signs and symptoms may happen:
- Foamy urine (protein in urine)
- Swollen feet, face and eyes
- Difficulties in breathing
- Tired and fatigue
- Poor appetite, nausea and vomiting
- Skin itchiness
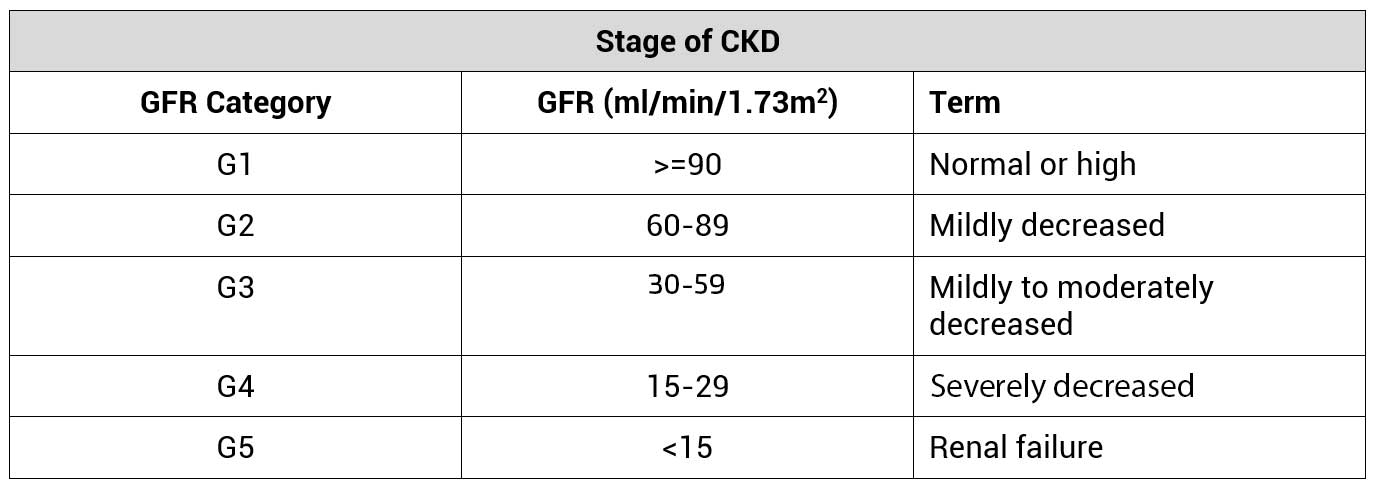
Stages of CKD
CKD is classified into 5 stages of severity. Stage 5 CKD is considered as End Stage Renal Disease (ESRD).
General measures in the management and delay progression of CKD

Identify the cause of Chronic kidney disease (CKD)

Encourage exercise, weight reduction and smoking cessation

Avoid excessive protein intake

Restrict sodium (salt) intake

Avoid NSAIDs and nephrotoxic drugs or unrecognized supplements/ herbal medicines

Optimize blood pressure and glucose control

Treat complications of chronic kidney disease (CKD), diabetes mellitus or hypertension